aCGT's third project of "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection" was approved by NMPA.
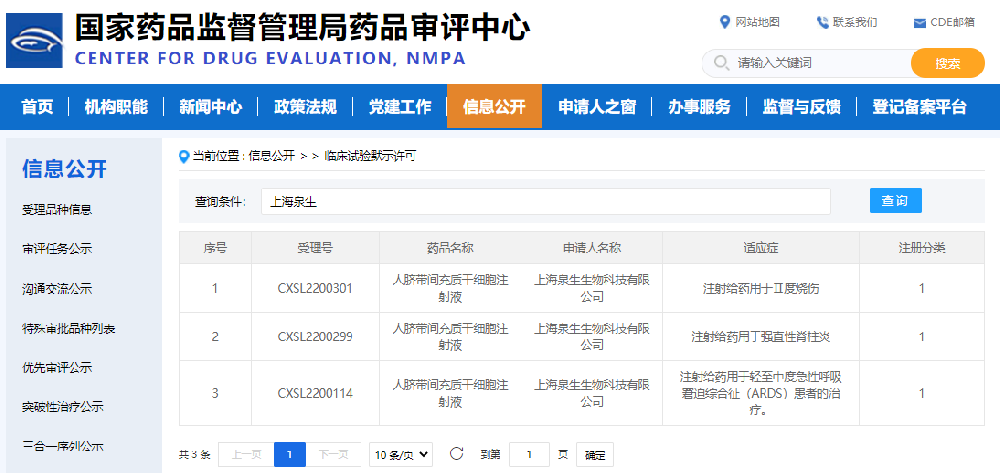
On September 14, 2022, aCGT's independently developed Class I biological product, "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection," has applied for clinical trial registration and obtained implied permission for clinical trials from the Drug Evaluation Center (CDE) of the National Medical Products Administration (NO.CXSL2200299, NO.CXSL2200301, NO.CXSL2200301). This is the third new registration after the approval of "acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS) and ankylosing spondylitis(AS)", which is mainly used for the treatment of second-degree burns. This marks that aCGT has made great strides into the leading position on the road of independent innovation in the research and development of new stem cell drugs in the country and even the world. 1、Introduction to indications - burns Burns are one of the common accidental injuries in clinical surgery, and it is also a disease that is easily overlooked and has a high morbidity and mortality. Most burns are caused by the heat of a hot liquid, solid, or fire, and are usually accompanied by an immunoinflammatory response that is difficult to treat, metabolic changes, and distributive shock, especially severe burns, which may eventually lead to failure of multiple organs. Many burn patients are not considered fully recovered even after the wound has healed, and the healed scar can affect the patient's appearance and self-confidence for a long time, bringing varying degrees of negative impact on the patient's life. At the same time, it affects the mental health, quality of life, ability to return to work, and in severe cases, even leads to death, leaving lifelong traces on the physical and psychological life of burn patients. It is estimated that about 100 million people worldwide are burned each year, and about 10% of burn injuries, or more than 10 million wounded, require hospitalization. After severe burns, the skin, as the first barrier of the human body's defense system, is destroyed, a large amount of water and electrolytes are lost, and the immune system is also damaged, resulting in disorders in the body's internal environment, hypovolemia resulting in insufficient perfusion of various tissues and organs, excessive free radical production, and the release of various inflammatory mediators, which aggravates the pathophysiological changes of the whole body and makes the condition more critical. Therefore, it is particularly important to accelerate wound healing and reduce complications after burns. Traditional treatment of burns: Typically, burn treatment consists of 5 strategies: surgical treatment, intensive care, wound care, adaptive nutrition, and aseptic isolation. In addition to early emergency treatment, skin grafting is currently a routine treatment method for patients with severe burns, but in clinical application, for patients with large-scale deep burns, autologous skin source cannot meet the needs of the body, and other substitutes including allogeneic skin, xenogeneic skin and various biological materials also exist such as transplant rejection, scar hyperplasia contracture, and no sweating function. The quality of life of patients is reduced, and the physical and psychological injuries are greatly harmed. Therefore, for the clinical treatment of burns, better treatment methods need to be developed urgently. Stem cells have strong proliferative ability and multi-directional differentiation potential, and studies have shown that the application of mesenchymal stem cells after burns can effectively inhibit the proliferation of inflammatory factors and promote the release of anti-inflammatory factors, thereby improving the local microenvironment of the injury and accelerating the healing of burn wounds. However, up to now, there are no stem cell products for burn indications on the market at home and abroad. Based on the pathological characteristics of burns and the advantages of mesenchymal stem cell therapy, Quansheng Biotech has developed human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection for the treatment of burns, which belongs to the first category of therapeutic biological products. Preclinical studies have suggested that human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection may have a variety of therapeutic effects such as inflammation regulation, angiogenesis and injury repair, and has good safety, and clinical application is expected to accelerate the recovery of burn patients, improve the prognosis of patients, and improve the quality of life of patients. 2、prospect Based on the regeneration, repair, immune regulation and paracrine characteristics of stem cells, aCGT’s "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection" can be used for the treatment of a variety of major and difficult diseases, including acute respiratory distress syndrome, burns and ankylosing spondylitis. The Class I biological product "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection", independently developed by aCGT, has completed preclinical pharmacy, pharmacology and toxicology studies in accordance with the requirements of Class 1 new drugs for therapeutic biological products, and can support it to enter clinical trials in terms of clinical needs, quality controllability, non-clinical efficacy and safety, and previous clinical safety. The three consecutive CDE clinical trials mark a major victory in the research and development of new drugs for the "Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Injection" of Quansheng Biotech. With the gradual opening of the scope of indications, aCGT will rely on its rich experience in drug application, start from the needs of patients, insist on launching new drug research and development, accelerate the application of new drugs for more refractory diseases, and further promote "human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell injection" for the treatment of more indications, so as to meet the "unmet clinical needs", with the ultimate goal of benefiting the majority of patients.